Alert Routing
Alert Routing allows you to configure Routing Rules to ensure that alerts are routed to the right responder with the help of event tags attached to them.
Prerequisites
-
The User Role associated with the user in the Team must have required permissions to manage Services (ability to manage Routing Rules).
-
Ensure you have
Tagsdefined for the Service.
Configuring Routing Rules
Ensure that the right Team is chosen from the team picker on the top of the screen.
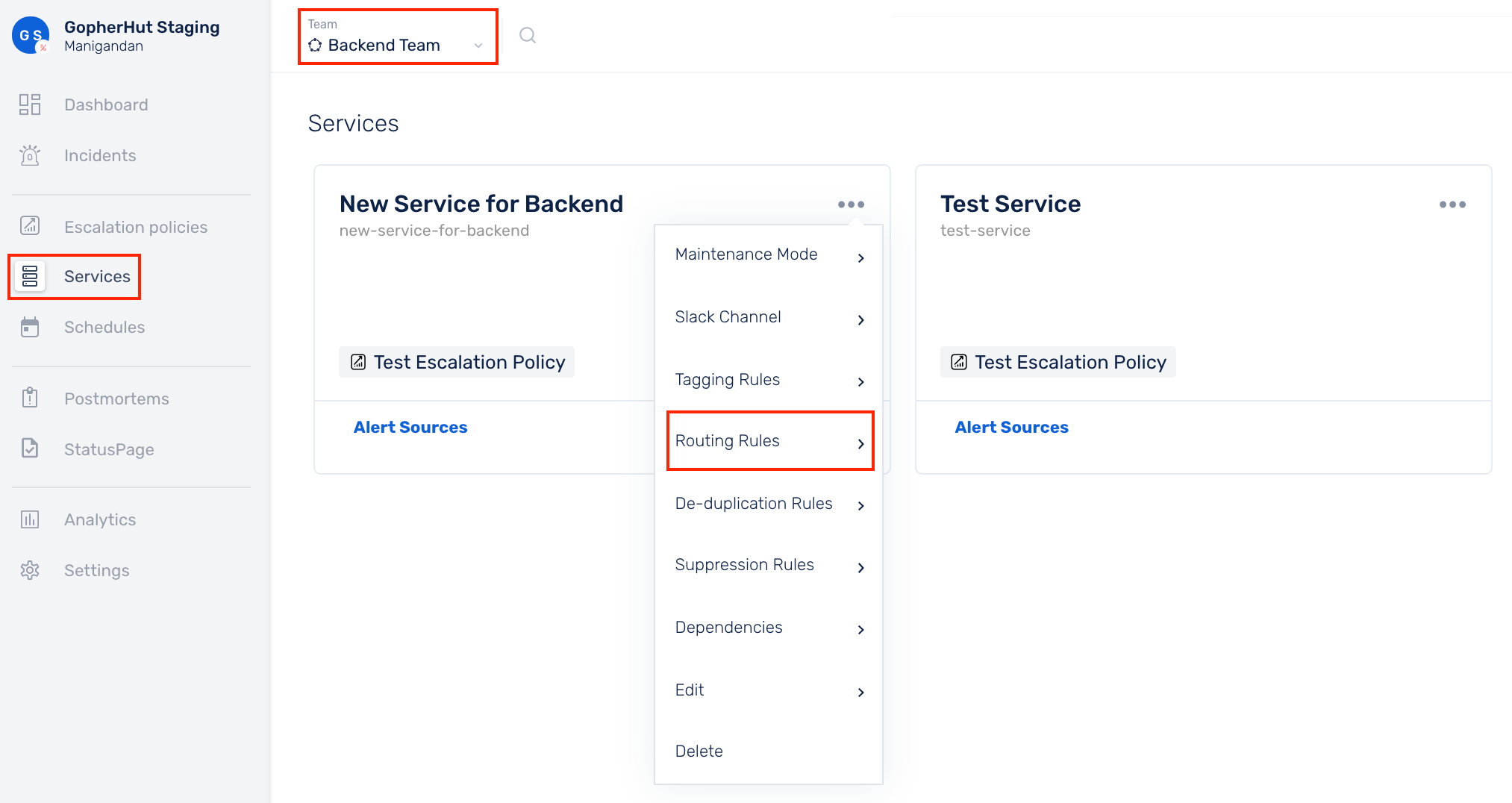
(1) Click on Services in the primary navigation
(2) For the Service of your choice, click on More options icon and select Routing Rules
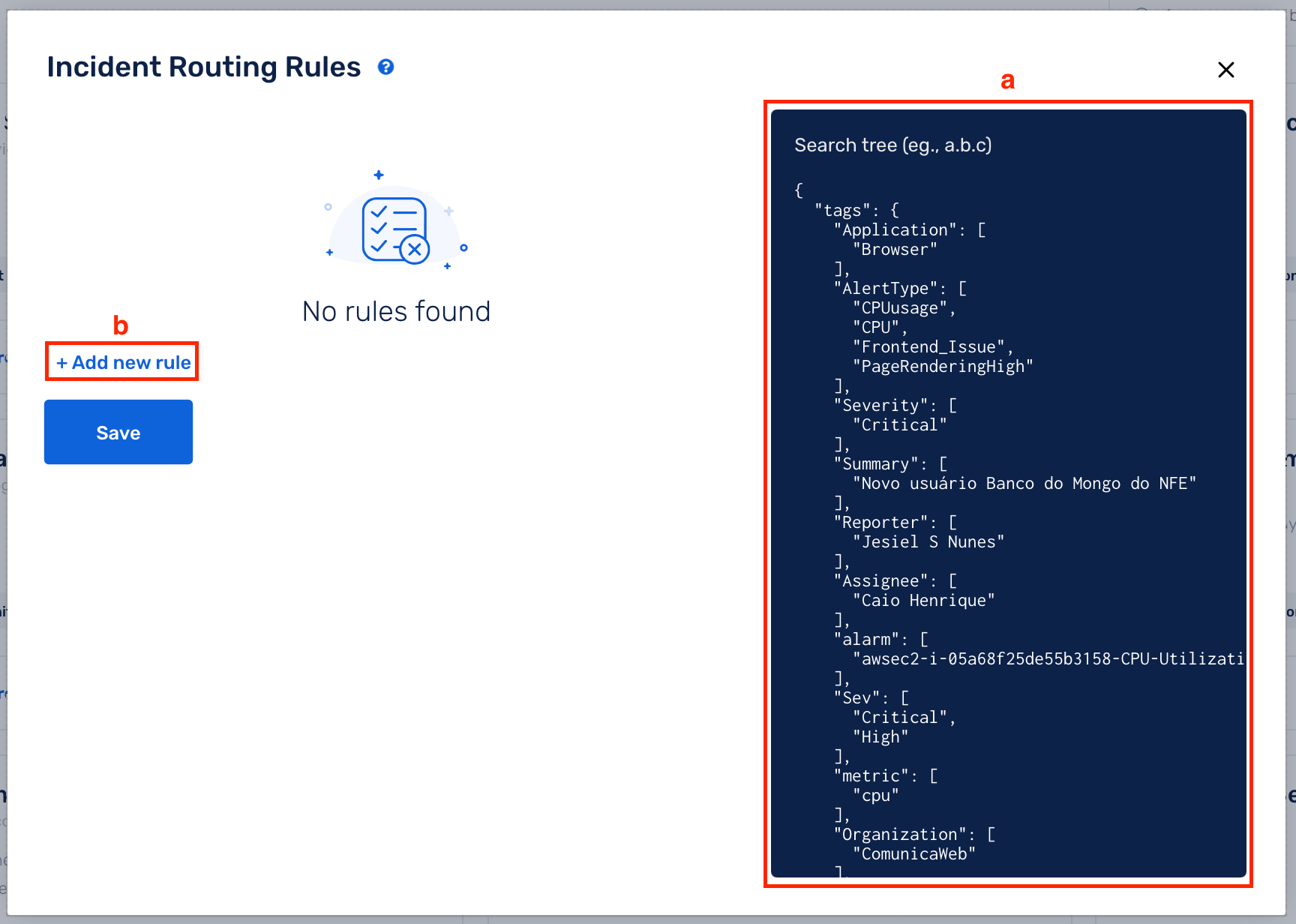
UI-based Rule Builder (Beginner-friendly)
(a) This box displays all the [event tags](https://support.squadcast.com/docs/event-tagging) defined for this Service, which can be used to define Routing Rules
(b) Select Add new rule
(c) Pick the event tag key and value pair that you are checking for in an incident using the drop-downs
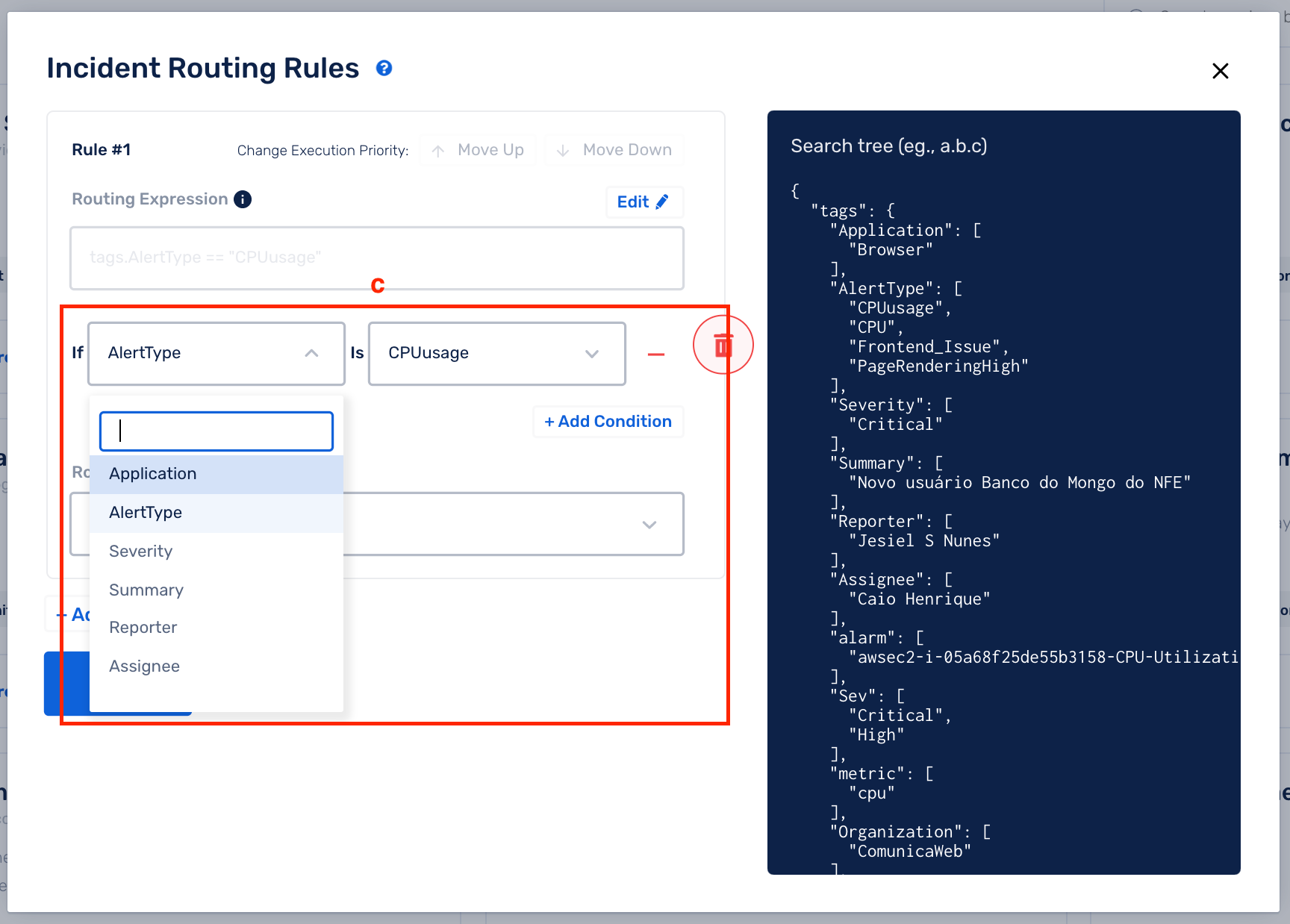
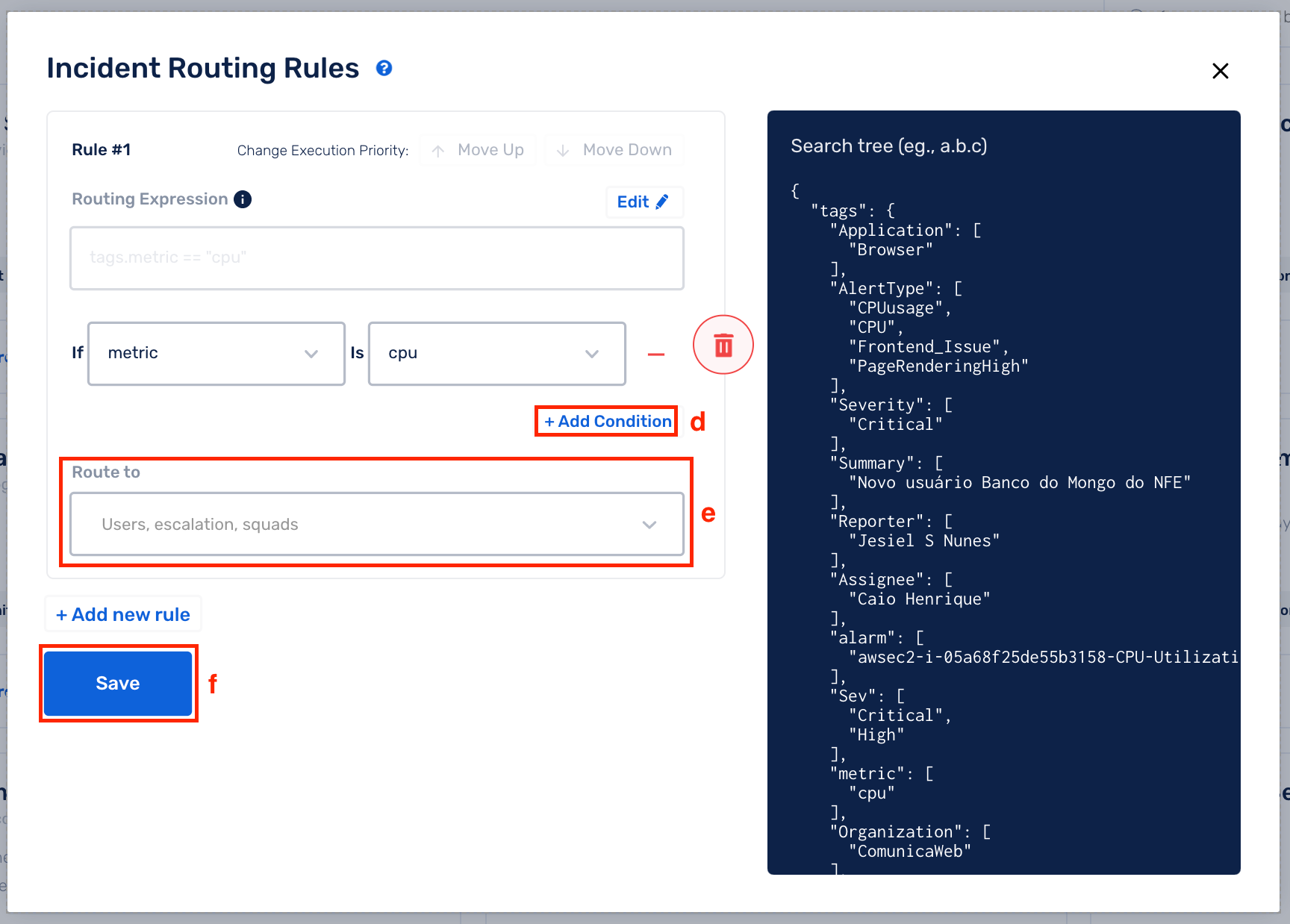
(d) Add Conditions to make your rules more granular
(e) You can route the incident containing the specific event tags to either a User, Squad or an Escalation Policy. Pick the same from the drop-down
(f) Click on Save
The Alert Routing Rules will take precendence (override) over the default Escalation Policy for the Service, if any of the rules match (evaluate to True) an incoming incident.
Raw String Method
Once you opt for the Raw String method, you cannot revert to the UI-based Rule Builder method for that rule.
(a) This box displays all the event tags defined for this Service
(b) Select Add new rule

(c) Click on Edit to enable Raw String method
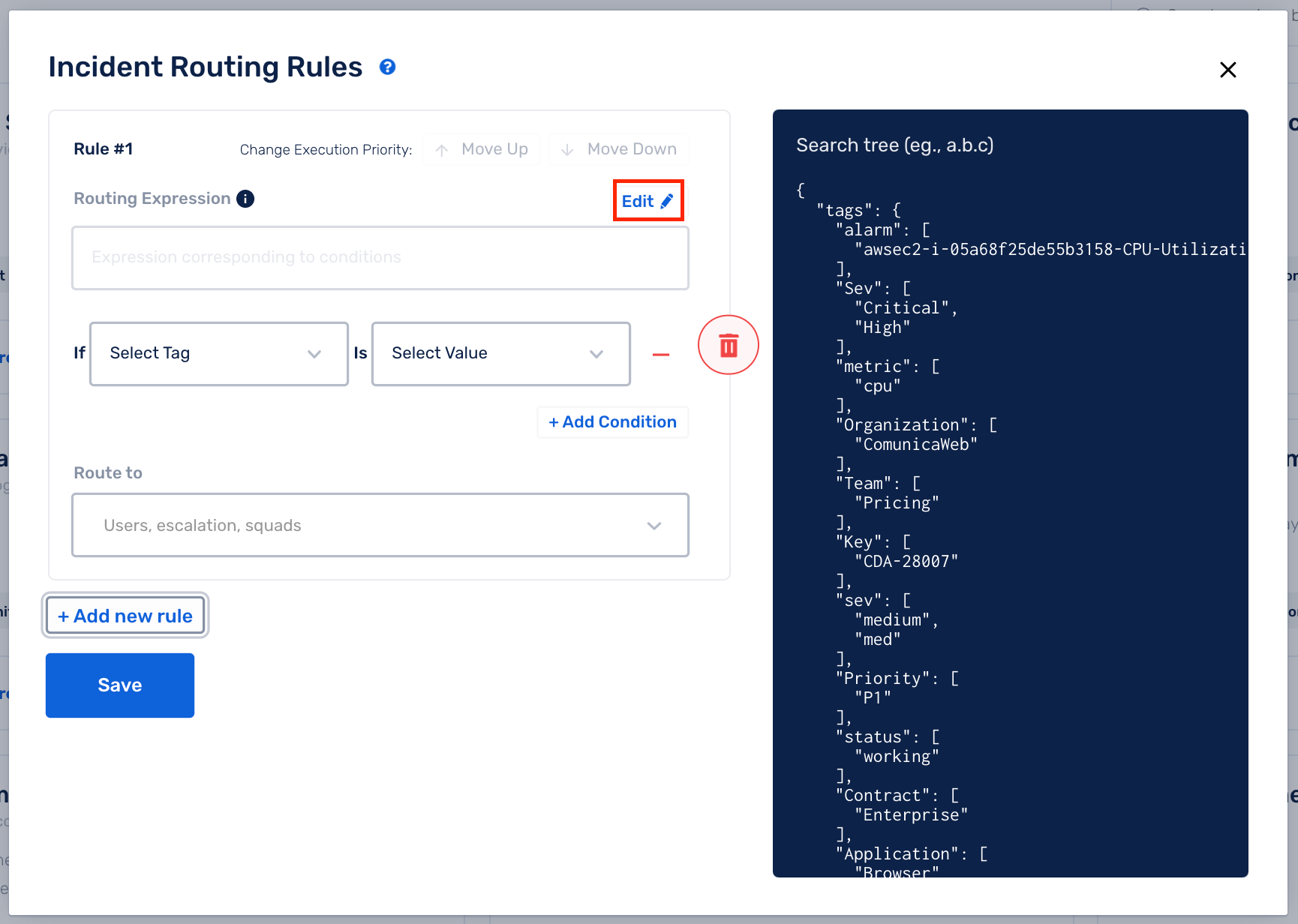
(d) Write your custom Tagging Rule expression and select Route To accordingly
(e) Click on Save
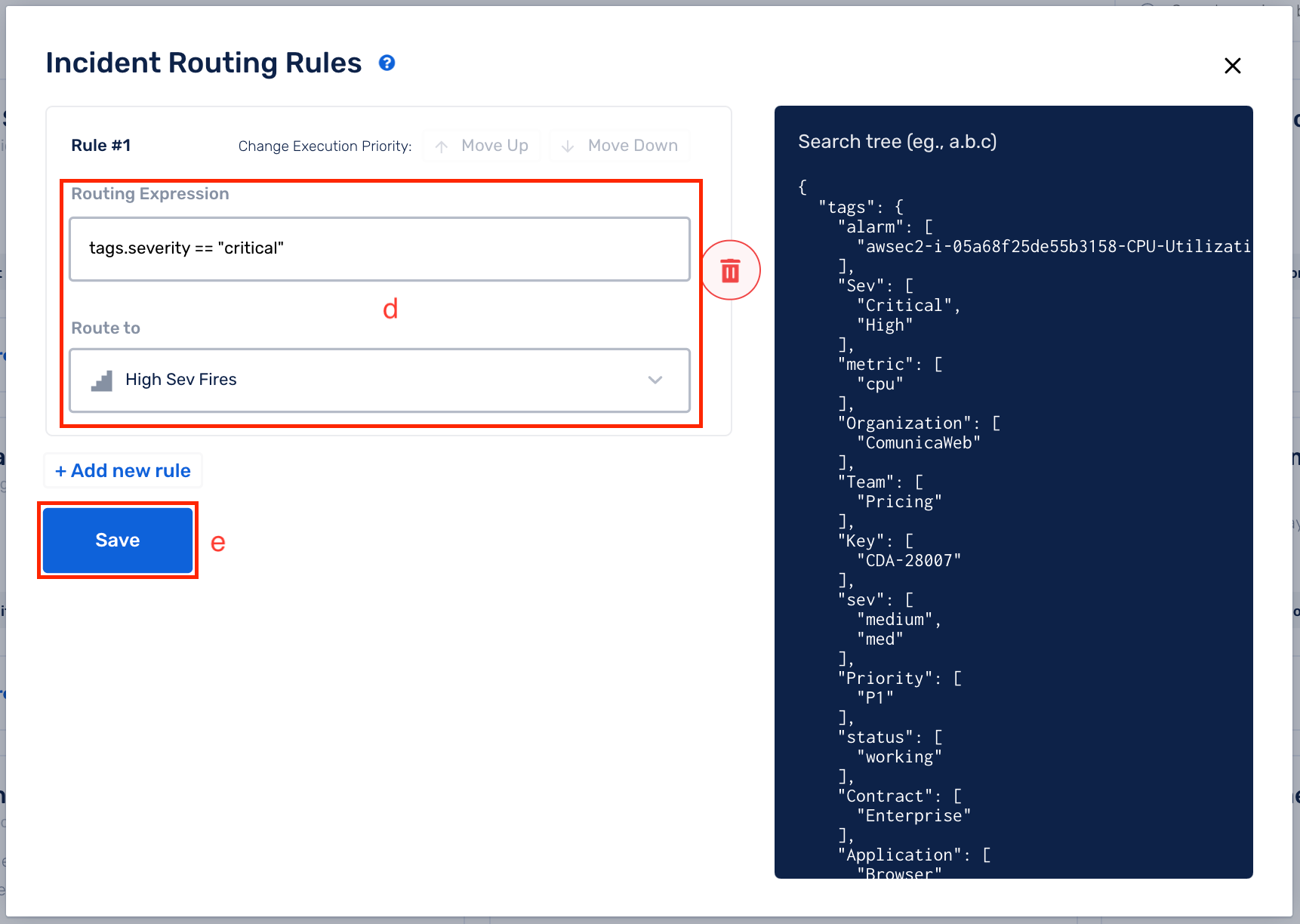
Supported Rules
The rule engine supports expressions with parameters, arithmetic, logical, and string operations.
Basic Expressions
10 > 0, 1+2, 100/3
Parameterized Expressions
tags.severity == "high"
The available parameters are tags
tags: This parameter contains the all the configured tags for a given Service.
Regular Expressions
re(tags.severity, "high.*")
This can be used to check if a particular tag field matches a regular expression.
Example
Below is the set of event tags defined for a Service (as shown in the right panel of the configuration space)
{
"tags": [
{
"severity": "critical"
},
{
"severity": "high"
},
{
"severity": "low"
}
]
}
Use-case for Routing Rules
When:
severityiscritical: Route to a Squadseverityishigh: Route to an Escalation Policyseverityislow: Route to a User
Routing Rules are as follows:
tags.severity == "critical"route to asquadtags.severity == "high"route to anescalation policytags.severity == "low"route to auser
FAQs
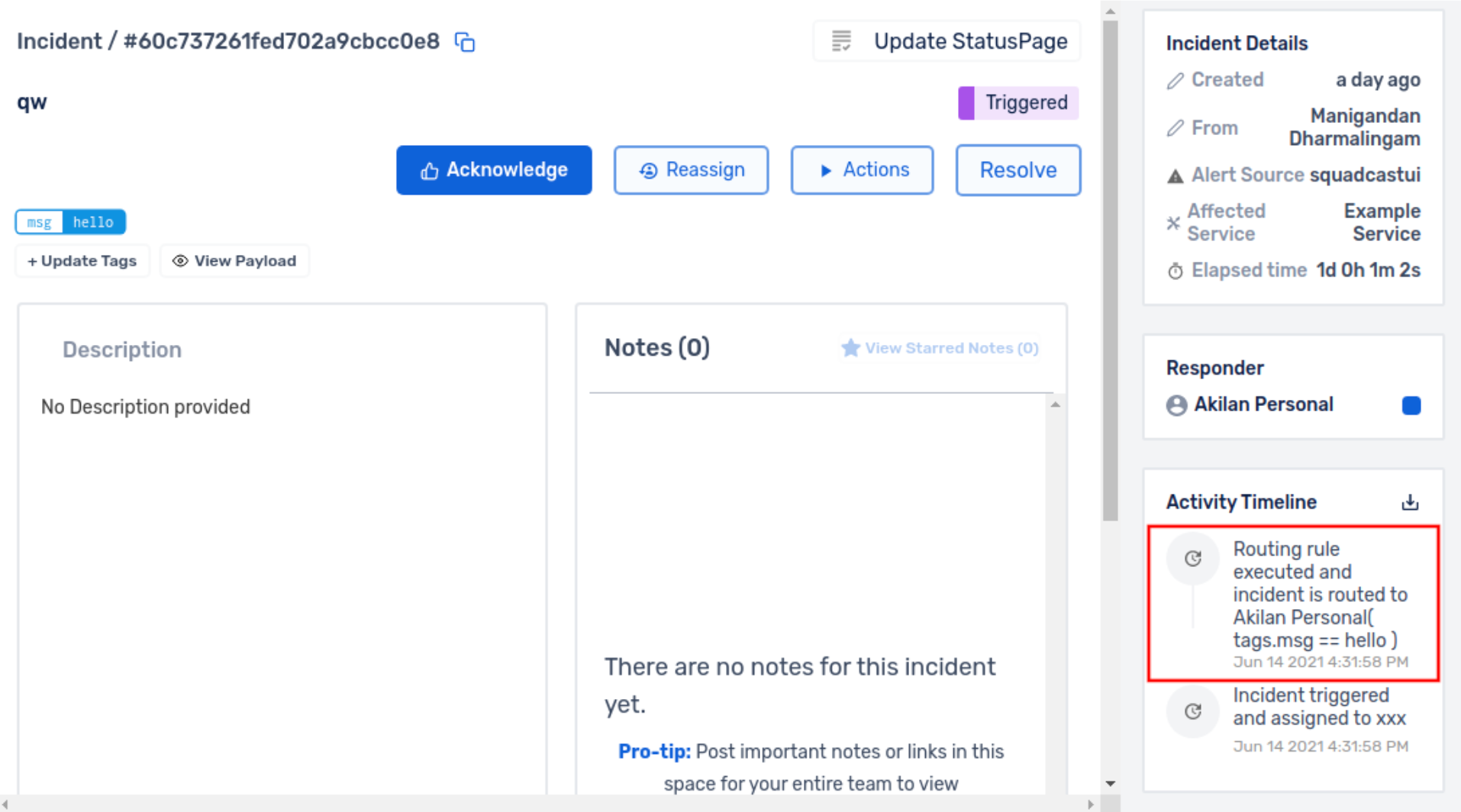
(1) How do I know if an incident gets routed due to a Routing Rule?
In the Incident’s Activity Timeline the reason for routing, and to which entity it gets routed to, is displayed.
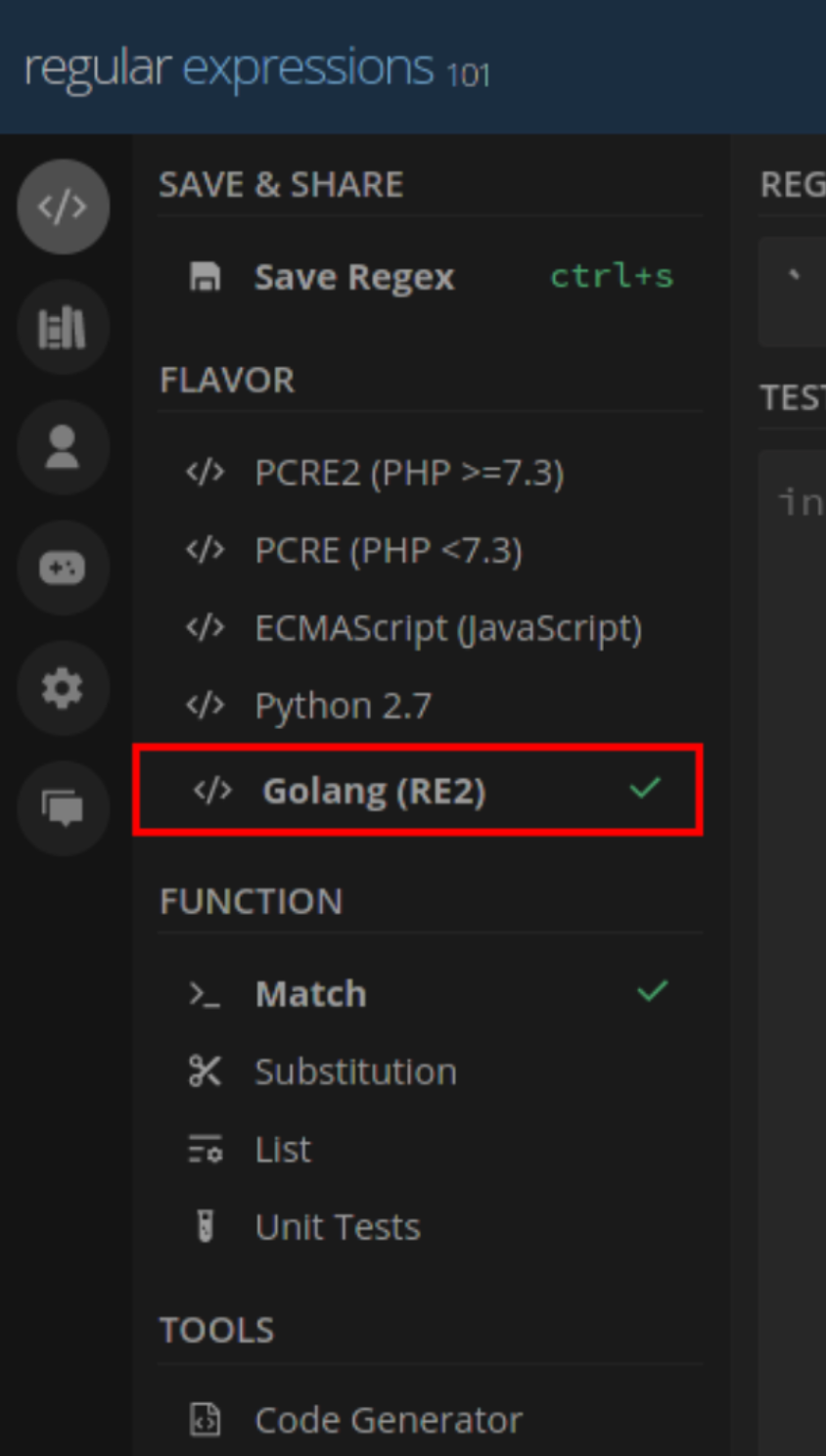
(2) What kind of regex can be used to write custom rules?
The rule engine supports expressions with parameters, arithmetic, logical, and string operations. You can also check this out to get an idea of all the expression types accepted in Squadcast. Please do your regex here against Golang flavour as shown in the screenshot below and then, set them up in Squadcast:
(3) Can I create OR rules?
Yes, you can. The evaluation between different Routing Rules is OR. Add multiple Routing Rules to enable OR evaluation.
(4) While adding a Routing Rule, is the search string in the rule case sensitive?
Yes, that is correct. For example, if your seach string is “ALERT” and your payload does not contain “ALERT” but contains “Alert”, this will not be matched. Your search string should be “Alert”.
(5) Do Routing Rules have priority?
Yes, you can specify Execution Rule Priority for the rules defined by moving them Up or Down the list of rules.

(6) I have configured multiple rules for a particular Service. Can I search through the configured rules to find the rule I am looking for?
Yes, that is doable. You will notice a Search option on the left-top of the rules modal. You can type in a word you recall from the rule. Any matching results will yield the narrowed down set of rules.
